|
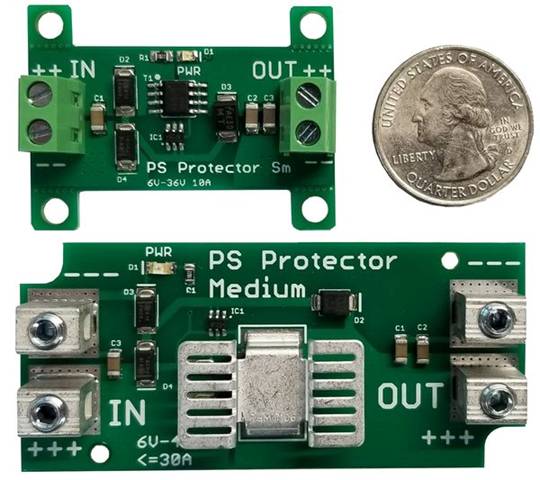
The PS Protector family is a range
of related products offered by Robot Power for the protection of AC/DC
power supplies used to power motors and motor controllers. The function of the PS Protector
family of products is to protect this type of power supply from reverse
current flow generated by electric motor Back-EMF. Battery power supplies can
generally just absorb a brief amount of reverse current without issues.
Features
|
PS Protector Inline Medium
·
Voltage: 6V - 48V
·
Current: 20A-30A
continuous, 60A peak
·
Size: 2.95" x
1.35" x .55"
·
Weight: 14g
·
Ideal diode function
·
Reverse current flow
protection
·
Reverse input polarity
protection
·
Inductive kickback
spike protection
·
Optional plastic
enclosure
|
PS Protector Inline Small
·
Voltage: 6V - 36V
·
Current 8A-12A
continuous, 25A peak
·
1.8" x 1.3" x
0.5"
·
Weight: 8g
·
Ideal Diode function
·
Reverse current flow
protection
·
Reverse input polarity
protection
·
Inductive kickback
spike protection
·
Mounts to ServoCity® Actobotics™
1.50" pattern mounting system
|
|
Buy it!
|
Buy it!
|
|

|

|
Documentation
·
PS Protector Small
drawing
·
PS Protector Medium
drawing
·
PS Protector Inline
Hookup Guide
·
PS
Protector Medium enclosure drawing
How it works
Due to the nature of electric motors, a rotating motor
generates a voltage of reverse polarity to that applied by the driving
motor controller. If this "Back-EMF" voltage is higher than
that applied to the motor by the motor controller it can cause a reverse
current flow from the motor to the power supply. The most common scenario for this
to occur is when the motor is operating near full speed and the motor
controller rapidly commands a lower power level. At full speed the motor is
generating Back-EMF nearly equal to the power supply voltage less losses
such as the load and friction.
When a sudden lower voltage is applied to the rotating motor
by the motor controller the driving voltage seen by the motor is reduced
before the mechanical motor rotation can catch up. This leaves the motor generating
the Back-EMF of its current rotation speed while the driving voltage from
the motor controller is at a lower level. This causes current to flow from
the higher voltage potential generated by the motor to the lower applied
by the motor controller i.e. back from the motor into the motor
controller and hence back into the power supply.
Due to the nature of the output regulation circuits in the
vast majority of AC/DC power supplies, attempted reverse current flow causes
the power supply to increase its output voltage to maintain current flow
out of the power supply. The
resulting voltage spike may be large enough to exceed the maximum ratings
of voltage sensitive circuits such as the power supply output regulation
circuit or the motor controller circuits. This can lead to the destruction
of the power supply or the motor controller or both.
The PS Protector family acts as an "Ideal Diode"
by using a low-resistance MOSFET to pass current in the forward direction
with very low losses but to instantly (a few nanoseconds) switch off the
MOSFET to block reverse current.
As soon as the output voltage level is lower than its input the PS
Protector turns the MOSFET on to allow normal current flow again.
A second function of the PS Protector family is to allow
multiple power supplies or battery supplies to power a load or for
multiple loads to use one power supply without interfering with each
other. Scenarios such as hot
swapping batteries or power supplies or seamless failover are also
supported by the PS Protector.
|